WATER
Water quantity and availability are among the most important natural-resource issues facing Kansans. The KGS is studying water issues and providing water information in a variety of forms.

Arikaree Breaks in Cheyenne County, part of the High Plains region.
High Plains Aquifer Evaluation
The Kansas Water Plan, legislation such as Senate Bill 287, and the Governor’s
Task Force on Water include requirements or needs for the State to provide
research and data for use in planning, policy, regulation, and protection
of the High Plains aquifer. KGS research has generated data, reports,
and maps that were placed on the High Plains Aquifer Information web site
(www.kgs.ku.edu/HighPlains/index.html),
most of which were also published as An Atlas of the Kansas High Plains
Aquifer (KGS Educational Series 14). The KGS is currently working on the
Ogallala Aquifer Support Study that is providing information supporting
recommendations of the Ogallala Aquifer Management Committee.
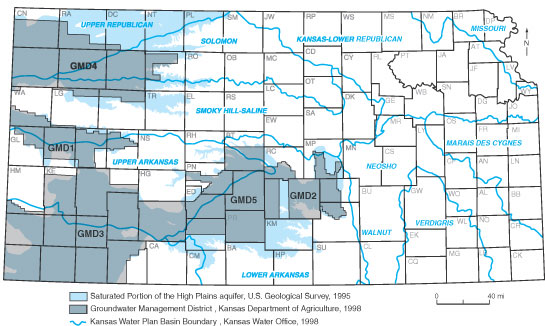
Location map showing High Plains aquifer extent, Groundwater District Management boundaries, and Kansas Water Plan basin boundaries, from Educational Series 14, 2000.
Surface-Water—Ground-Water Interactions
The Kansas Water Plan includes water planning and management strategies
for each drainage basin, strategies that require knowledge of the interactions
between surface water and ground water. With funding from the U.S. Department
of Agriculture and Texas A&M University, the KGS recently completed
the integration of computer models for surface- and ground-water hydrology.
Hydraulic characterization of the stream-aquifer interface is being conducted
in cooperation with the University of Nebraska and is supported by a competitive
U.S. Geological Survey grant. A stream-aquifer interaction investigation
has been initiated in the middle Arkansas River corridor in cooperation
with the Subbasin Water Resources Management Program of the Kansas Department
of Agriculture.
Water-resources Sustainability and Aquifer
Recharge
State and local agencies have recognized the importance of sustainable
development of water resources in Kansas. A key consideration in balancing
the water budget is knowledge of aquifer recharge, or movement of water
back into aquifers. In a cooperative research project with the U.S. Geological
Survey and Kansas State University, the KGS is quantifying ground-water
recharge deep in the High Plains aquifer using state-of-the-art sensors.
A recharge study supported by Texas will be valuable for better quantification
of aquifer recharge in Kansas.
Aquifer-site Characterization
The accurate assessment of the threat that a ground-water contamination
site poses to nearby water users depends on the quality of the information
obtained through field investigations. The KGS is developing and refining
field methodologies used in site characterization. These include slug-test,
direct-push, and hydraulic tomography technologies for the characterization
of preferential flow paths, zones in which a contaminant moves much faster
than the average hydraulic conductivity of the water-bearing formation.
Another approach is the application of a moving mesh technique for ground-water
modeling of contamination plumes. This work is conducted in cooperation
with governmental and private entities and other universities and includes
support by competitive U.S. Geological Survey and National Science Foundation
grants.
Contaminant Distribution and Fate in Ground
Water
Protection of the quality of Kansas’ water resources from contamination
by nitrate and other substances is a high priority. KGS researchers are
using nitrogen isotopes to identify sources of nitrate (e.g., agrochemicals,
animal and human wastes, soil nitrogen) that contaminate ground waters.
Recent projects identifying sources and determining nitrate distribution
have been conducted for the Kansas Department of Health and Environment
(KDHE), a groundwater management district, and cities. Other studies include
development of GIS tools for assessing potential impacts of pesticide
use on ground-water quality for the Kansas Department of Agriculture and
determination of the source area of water contributing to the spring discharge
used for the water supply of Florence.
Salinization of Water Resources
Multiple sources of salinity degrade the quality of water resources in
Kansas, including natural saltwater discharged from bedrock, dissolved
solids concentrated by evapotranspiration, and wastewaters such as oil
brine and water-softener discharge. The KGS recently completed a Kansas
Water Plan project evaluating the transport of saline Arkansas River water
contaminating the ground-water resources of the High Plains aquifer in
the river corridor. A salt-assessment study was conducted for the KDHE.
Recent investigations of saltwater-source identification also have been
carried out for the Kansas Department of Agriculture and Kansas Corporation
Commission.

Salt-assessment study.
Statistical Analysis of High Plains Aquifer
Water Levels
Each January, water levels are measured in wells in western Kansas. A
statistical technique is used to detect erroneous values that should be
remeasured in a second round of measurement. The analysis also detects
wells with aberrant conditions that may affect the reliability of measurements
and identifies other sources of error to be corrected in subsequent years.
Geostatistical analyses identify “holes” in the observation-well
network where the uncertainty in water-table elevations exceeds allowable
limits and where additional observation wells are needed.

Aquifer-site characterization study on the Arkansas River near Larned.
List of 2002 Publications—Water References
Kansas Geological Survey
Online May 20, 2003
Comments to: webadmin@kgs.ku.edu
URL:http://www.kgs.ku.edu/Publications/AnnRep02/water/water.html
