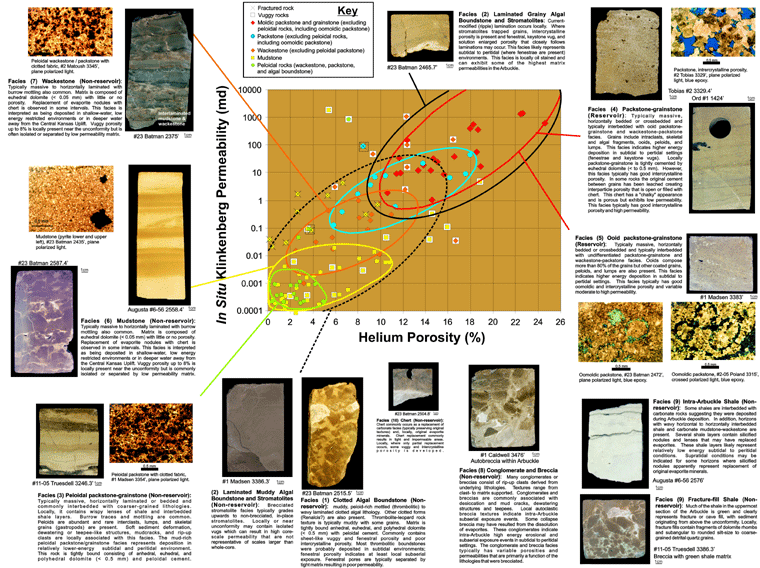
Arbuckle Core Characteristics
- Relative lack of karst associated fracture, breccia, and dissolution porosity in most cores - especially surprising considering that the cores came from flanks or tops of structural highs where karst processes would likely have been most extensive
- Dominance of matrix porosity (intercrystalline, moldic, fenestral, vuggy) related to depositional facies, early diagenesis, and dolomitization
Lithofacies
Major facies include:
- Clotted algal boundstone
- a) laminated muddy algal boundstone, b) laminated grainy algal boundstone
- peloidal packstone-grainstone
- packstone-grainstone
- ooid packstone-grainstone
- mudstone
- wackestone
- intraclastic conglomerate and breccia
- cave fill shale and depositional shale
- chert
In the cores studied the first seven lithologies account for more than 85% of the cored intervals.
Click on Facies to bring up more detail
|
|
e-mail : webadmin@kgs.ku.edu
Last updated June 2003
http://www.kgs.ku.edu/PRS/publication/2003/ofr2003-32/P3-04.html
