2003 Annual Water Level Raw Data Report for Kansas
Prev Page--Report Start || Next Page--Acquisition Activity
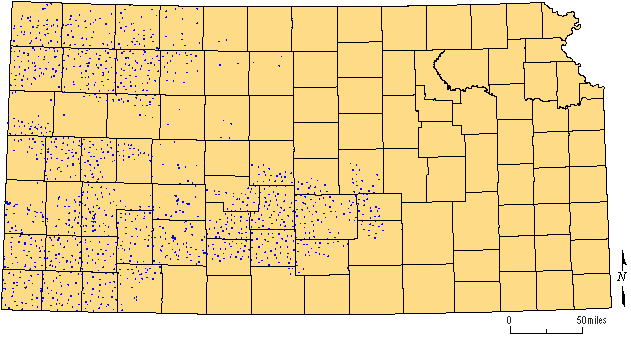
The Division of Water Resources (DWR) of the Kansas Department of Agriculture and the Kansas Geological Survey (KGS) manage and operate the statewide cooperative annual water level measurement program. Water level measurements are scheduled annually for about 1,350 wells spread across 47 central and western Kansas counties (Figure 1). These annual measurements are nominally made during the month of January and include wells used for stock, irrigation, household, and monitoring (some abandoned agricultural or domestic wells). The data acquired during these yearly measurements are tabulated to establish trends and allow evaluation and judgments for effective water resource management.
Figure 1--Locations of wells in 2003 water-level measurement program.

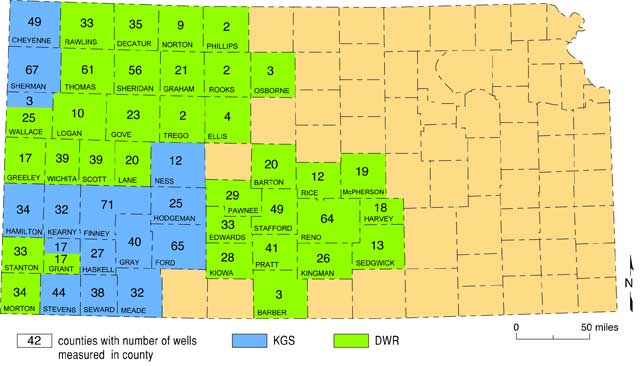
The KGS and DWR share responsibility for acquiring annual water levels. The KGS measures 504 wells in 15 counties while DWR has responsibility for 844 wells in 34 counties (two counties are shared) (Figure 2). Most wells in the network (73.7%) are currently used for irrigation. During 2003, 94.7% of all annual network wells were successfully measured. Approximately half of these measurements (45.6%) encountered water at depths of less than 100 ft. About 2.00% of network wells have depths to water greater than 300 ft (up from 1.77% in 2002 and 1.78% in 2001). At the present time 1,198 of the 1,348 annual network wells have GPS-measured latitudes and longitudes. This means that 88.87% of the program wells have a GPS stamp; this is down from 99.19% and 99.85% in 2002 and 2001, respectively, but up from 46.74% for the 2000 acquisition year. After completion of the 2003 measurement season, 18 network wells have been targeted for retirement due to plugging, surface or downhole obstructions, inaccessibility to the water surface as a result of changes in measurement point, destruction, or "dry hole." Attempts over the last three years to fill holes in the network represent the first increase in the High Plains Aquifer's annual well inventory since the mid-1980s. Reduction of the sampling holes by the yearly incorporation of enhancement wells will be an ongoing process that will be based on number and location of wells retired from the network each year. Digital and analog 2003 annual raw water level data were available for widespread distribution around March 1, 2003.
Figure 2--Number and organizational responsibility by county for the 2003 network wells.
Data acquisition enhancements evaluated or refined during the 1999-2002 campaigns were incorporated into the 2003 KGS program. DWR changes included the initial use of computers running the WaterWitch software for several hydrographers in 1999 and the initial use of the Palm Pilot 3 with the Water Bug program for enhanced data collection in 2001. The most significant enhancement for KGS was the inclusion of a seventh person functioning as a troubleshooter and enhancement/replacement well investigator beginning in 2000. The seventh person operates alone, following the three two-man crews, doing remeasurements of wells that are out of trend as well as locating and measuring wells previously selected as candidate enhancement or replacement wells. Use of the KGS-developed, computerized data acquisition system (WaterWitch) permitted on-site entry of measurements and comments, automated checks of data quality, optimized routing, and the encryption of a location stamp on each measurement. Improved routing and the computerized acquisition system have steadily reduced data acquisition time from 8 days in 1997 to 5 days for 2003 for the three two-person crews. Improvements in training/technique and routing increased the 13 wells/person/day measured in 1998 to 17 wells/person/day measured in 2003. Insight gained through statistical analyses of the 10% remeasurement wells (QA) continued in 2003 to prove invaluable in both improving our product and in determining the overall quality of the measurement data. Revisits and remeasurement of wells classified as out-of-trend during initial measurements (QC) improved confidence and minimized measurement errors in the database.
Data acquisition enhancements evaluated during the 2000, 2001, and 2002 campaigns included the introduction of a paperless data entry system centered around a small (3"x5"x1/2") handheld computer, the Palm Pilot 3, running custom in-house software. Results from 2000 showed this system to be an extremely effective and a highly efficient data acquisition/recording tool, so this system was supplied to and used by several members of the DWR crew during the 2003 data collection campaign.
Spatial analysis of the 2002 water level data identified 13 locations where new wells should be incorporated into the annual measurement network to eliminate sampling "holes." Cooperation between the groundwater management districts (GMDs), DWR, and KGS staff identified wells acceptable for inclusion in the network at all locations. All 13 sites resulted in water level measurements in 2003, and a procedure is now in place for the incorporation of new wells into the annual network, allowing overall completeness of sampling to improve each year. The last five years have seen positive growth in the number of wells in the annual network in response the retirement or replacement of inconsistent, plugged, or inaccessible wells.
The Quality Control program continues to achieve its objectives of identifying and quantifying sources of unwanted variation in observation well data collection, and in flagging wells whose measurements require verification. In 2000 and 2001, most of the possible sources of unwanted variation were not significant, in strong contrast with results obtained in 1999 when most exogenous variables were significant. QC for the 2002 and 2003 data acquisition is remarkably free of inconsistencies compared to previous field seasons. The results can be interpreted as reinforcing the need for training and the desirability of deleting troublesome wells from the monitoring program. As the Quality Control process continues to be applied to the KGS observation well measurement program in the future, and particularly if it is applied to the entire Kansas observation well network, the quality of the groundwater measurement data is expected to improve over time (Davis, 2002).
The original observation well network designed in 1984 was based on a regular hexagonal pattern, with observation wells located at or near the centers of the hexagons. Unfortunately, some current observation wells are far from the centers of their hexagons, and some hexagons no longer contain a network well at all, resulting in "holes" in the network. The integrity of the network is being restored through the selection and measurement of new wells optimally located to fill existing undersampled areas. Determining the very best places for replacement wells requires a geostatistical study, which unfortunately delays the measurement of the water surface in undersampled areas. Replacement wells selected by measurement staff during the measurement campaign are preferred over leaving a "hole" in the network for that measurement year while waiting for a computer-aided replacement well to be selected for the following year. A good rule of thumb for field workers to use for selecting a replacement for a lost observation well is to choose a new well as close as possible to the center of the hexagon. It is possible to have holes form in the network if replacement wells deviate too far from the center of the hexagon. Yearly geostatistical studies will define undersampled areas (holes) and select optimum locations for replacement wells to eliminate extraneous holes in the network occasionally left by the hexagon system.
Prev Page--Report Start || Next Page--Acquisition Activity