| Facies code |
Lithofacies | Sedimentary structures | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gms | massive, matrix supported gravel | grading | debris flow deposits |
| Gm | massive or crudely bedded gravel | horizontal bedding, imbrication | longitudinal bars, lag deposits, sieve deposits |
| Gt | gravel, stratified | trough crossbeds | minor channel fills |
| Gp | gravel, stratified | planar crossbeds | linguoid bars or deltaic growths from older bar remains |
| St | sand, medium to v. coarse, may be pebbly | solitary (theta) or grouped (pi) trough crossbeds | dunes (lower flow regime) |
| Sp | sand, medium to v. coarse may be pebbly | solitary (alpha) or grouped (omikron) planar crossbeds | linguoid, transverse bars, sand waves (lower flow regime) |
| Sr | sand, very fine to coarse | ripple marks of all types | ripples (lower flow regime) |
| Sh | sand, very fine to very coarse, may be pebbly | horizontal lamination, parting or streaming lineation | planar bed flow (l. and u. flow regime) |
| Sl | sand, fine | low angle (< 10 degrees) crossbeds | scour fills, crevasse splays, antidunes |
| Se | erosional scours with intraclasts | crude cross-bedding | scour fills |
| Ss | sand, fine to coarse, may be pebbly | broad, shallow scours including eta crossbedding | scour fills |
| Fl | sand, silt, mud | fine lamination, very small ripples | overbank or waning flood deposits |
| Fsc | silt, mud | laminated to massive | backswamp deposits |
| Fcf | mud | massive, with freshwater molluscs | backswamp pond deposits |
| Fm | mud, silt | massive, dessication cracks | overbank or drape deposits |
| Fr | silt, mud | rootlets | seatearth |
| C | coal, carbonaceous mud | plants, mud films | swamp deposits |
| P | carbonate | pedogenic features | soil |
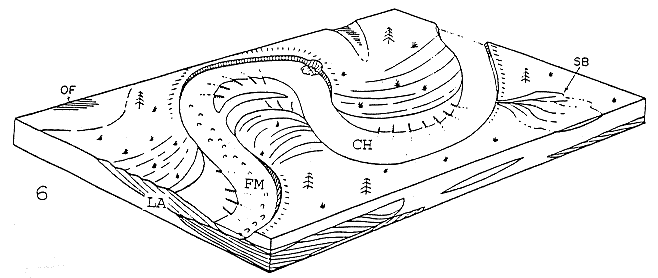
Model 6--the classic sandy, mixed-load meandering river.

Architectural elements in fluvial deposits
| Element | Symbol | Principal lithofacies assemblage |
Geometry and relationships |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channels | CH | any combination | finger, lens or sheet; concave up erosional base; scale and shape highly variable; internal concave-up secondary erosion surfaces common |
| Gravel bars and bedforms | GB | Gm, Gp, Gt | lens, blanket; usually tabular bodies; commonly interbedded with SB |
| Sandy bedforms | SB | St, Sp, Sh, Sl, Sr, Se, Ss |
lens, sheet, blanket, wedge; occurs as channel fills, crevasses, splays, minor bars |
| Foreset macroforms | FM | St, Sp, Sh, Sl, Sr, Se, Ss |
lens resting on flat or channelled base, with convex-up second-order internal erosion surfaces and upper bounding surface |
| Lateral accretion deposits | LA | St, Sp, Sh, Sl, Se, Ss; less commonly Gm, Gt, Gp | wedge, sheet, lobe; characterized by internal lateral accretion surfaces |
| Sediment gravity flows | SG | Gm, Gms | lobe, sheet; typically interbedded with GB |
| Laminated sand sheets | LS | Sh, Sl; minor St, Sp, Sr | sheet, blanket |
| Overbank fines | OF | Fm, Fl | thin to thick blankets; commonly interbedded with SB; may fill abandoned channels |
Please use the "Back" command of your browser to return to the page you were viewing.
Dakota Home || Start of the Stochastic Modeling Report